As we enter the busy tax season, it is important to understand the different types of tax forms that are out there. One of the forms that many of us may encounter is the 1099 form, which reports income other than wages, salaries, and tips. Let’s take a closer look at this form and how it differs from other tax forms.
Why do I receive a 1099 form?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1099r-eda9fdcb4d82449da27f9f30a318aaa3.jpg) There are many types of income that are reported on a 1099 form, including:
There are many types of income that are reported on a 1099 form, including:
- Self-employment income
- Rental income
- Investment income
- Unemployment compensation
- Social Security benefits
- And more
If you receive any of these types of income throughout the year, you may receive a 1099 form from the payer. The form will detail how much income you received and may also include any taxes withheld.
What is the difference between a 1099 form and a W-2 form?
 The biggest difference between a 1099 form and a W-2 form is that a W-2 form is used to report employee wages and salaries, while a 1099 form is used to report other types of income.
The biggest difference between a 1099 form and a W-2 form is that a W-2 form is used to report employee wages and salaries, while a 1099 form is used to report other types of income.
When you work as an employee, your employer withholds taxes from your paycheck and sends that money to the government on your behalf. At the end of the year, your employer sends you a W-2 form, which shows how much money you earned and how much money was withheld for taxes.
On the other hand, when you receive income that is reported on a 1099 form, the payer does not withhold taxes from your income. You are responsible for paying any taxes owed on this income on your own.
How do I report income on a 1099 form?
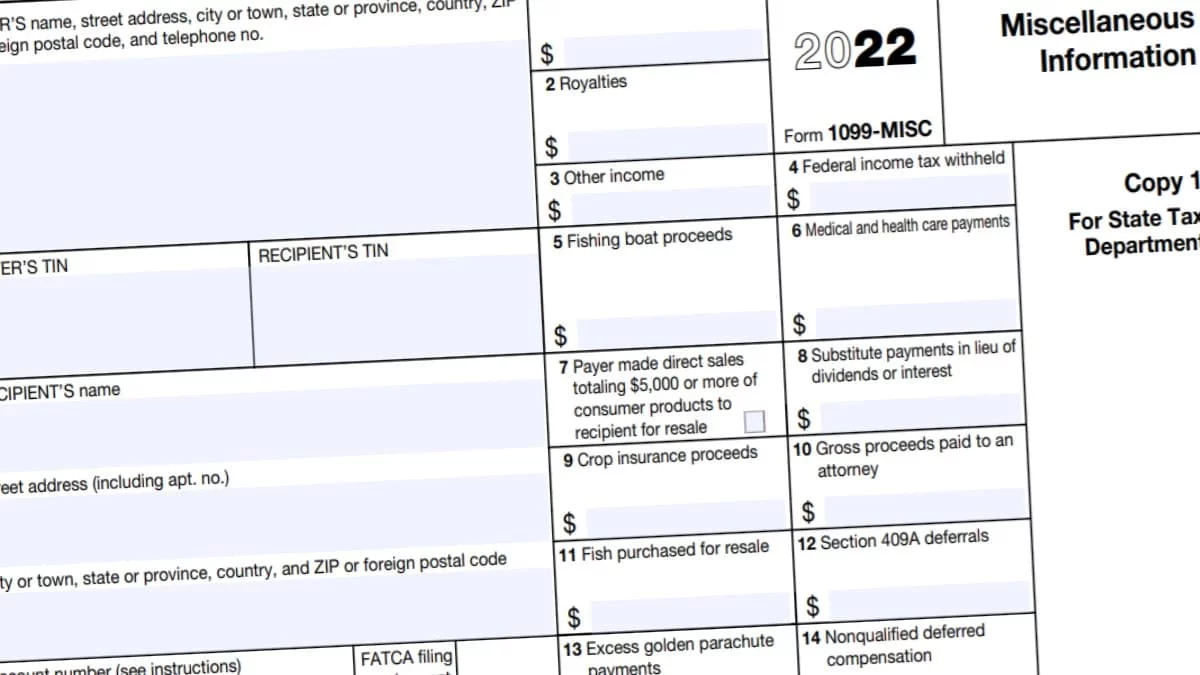 When you receive a 1099 form, you need to report the income on your tax return. The amount of tax you owe will depend on your total income for the year and your tax bracket.
When you receive a 1099 form, you need to report the income on your tax return. The amount of tax you owe will depend on your total income for the year and your tax bracket.
If you receive multiple 1099 forms, you will need to report the total of all the income on your tax return.
It is important to keep accurate records of your income throughout the year so that you can properly report your income on your tax return.
Are there different types of 1099 forms?
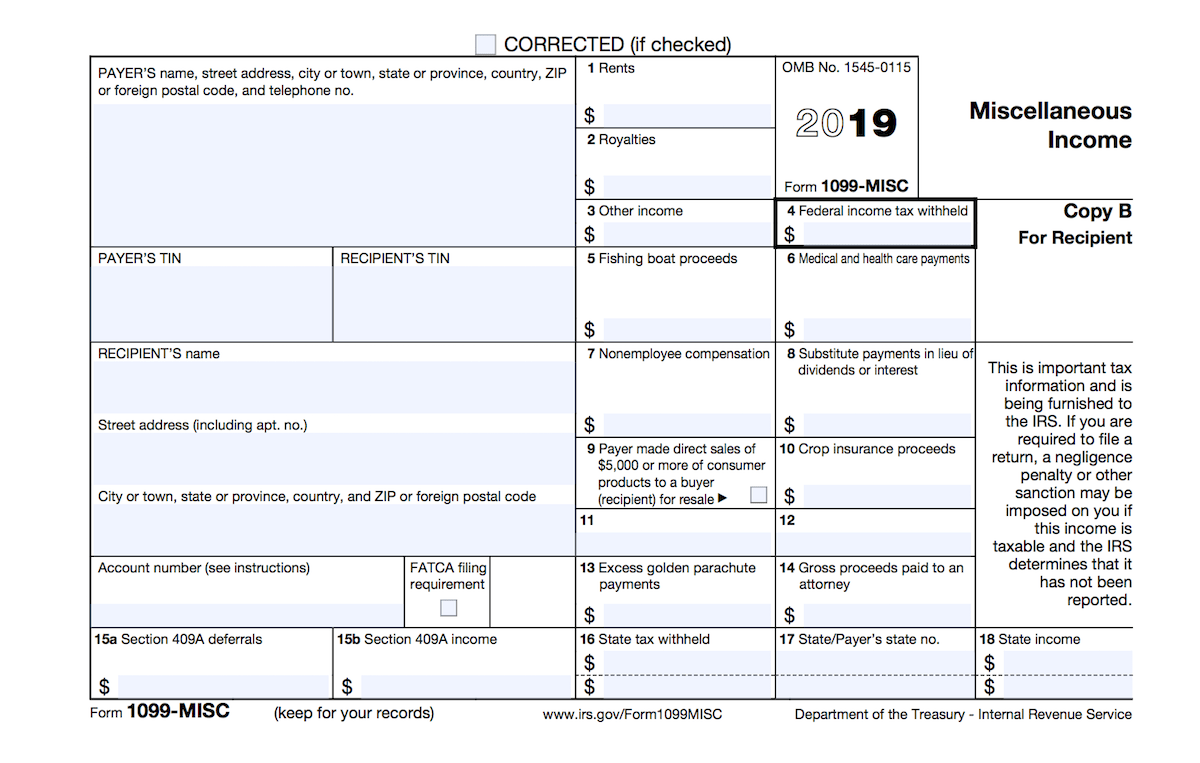 Yes, there are several different types of 1099 forms, including:
Yes, there are several different types of 1099 forms, including:
- 1099-MISC: Used to report miscellaneous income, such as self-employment income, rental income, and royalties
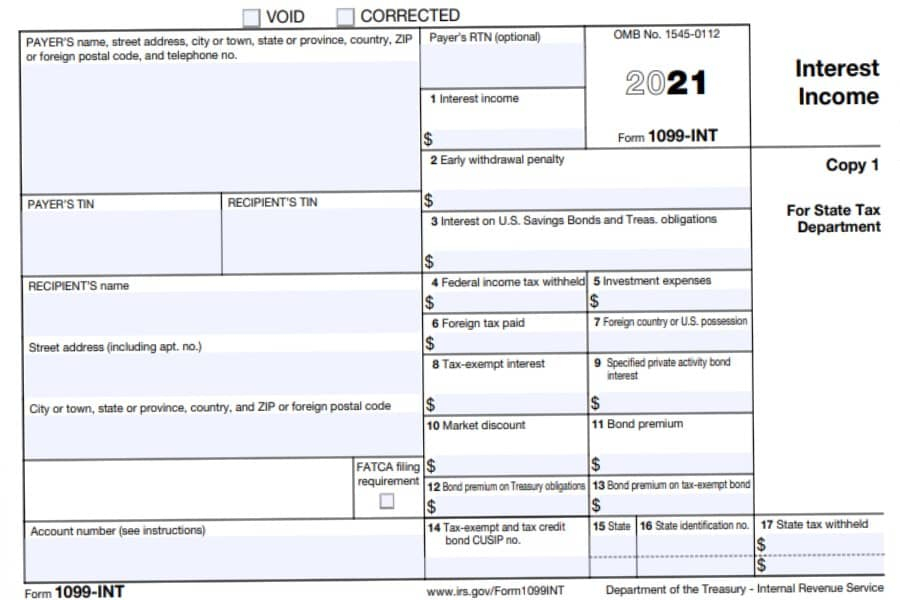
- 1099-INT: Used to report interest income, such as interest from a savings account or bond
- 1099-DIV: Used to report dividend income, such as dividends from stocks or mutual funds
- 1099-B: Used to report sales of stocks, bonds, or other investments
- And more
The specific type of 1099 form you receive will depend on the type of income you received.
Can I receive both a W-2 and a 1099 form?
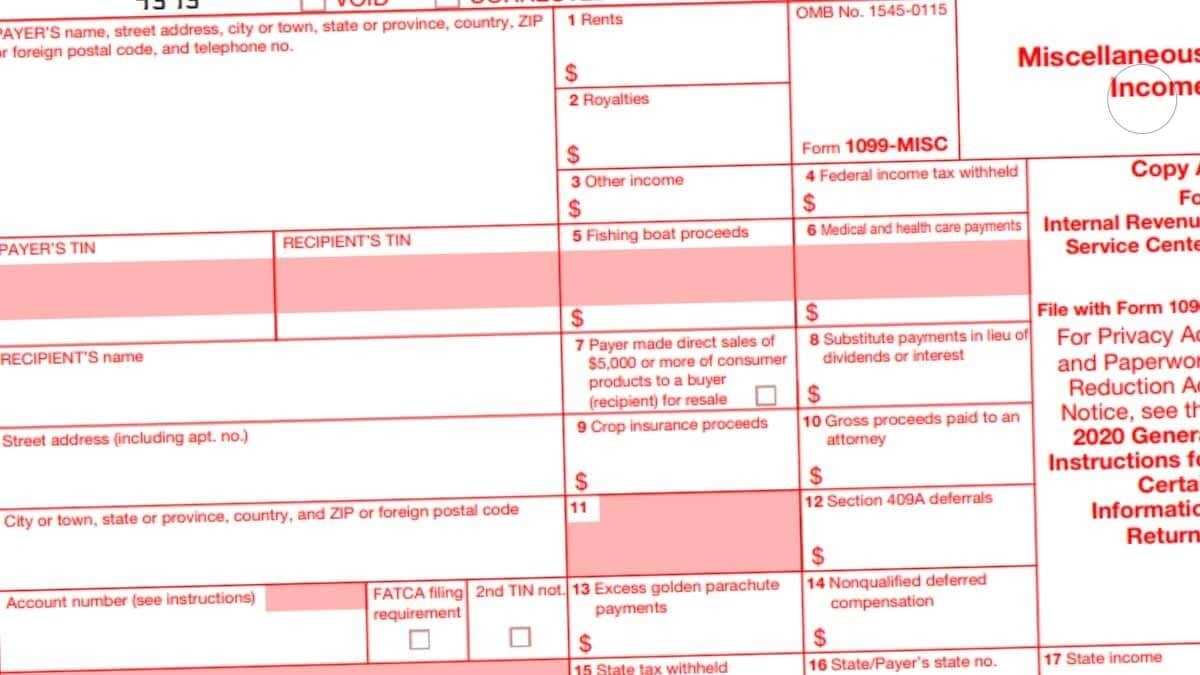 Yes, it is possible to receive both a W-2 form and a 1099 form in the same tax year. For example, if you have a full-time job and also freelance on the side, you may receive a W-2 form from your employer and a 1099 form from your freelance clients.
Yes, it is possible to receive both a W-2 form and a 1099 form in the same tax year. For example, if you have a full-time job and also freelance on the side, you may receive a W-2 form from your employer and a 1099 form from your freelance clients.
If you receive both a W-2 form and a 1099 form, be sure to include both types of income on your tax return.
What are some tips for dealing with 1099 forms?
 Dealing with tax forms can be daunting, but here are some tips to make it easier:
Dealing with tax forms can be daunting, but here are some tips to make it easier:
- Keep accurate records of all income you receive throughout the year
- Stay organized by keeping all of your tax forms in one place
- Consider working with a tax professional who can help you navigate the complexities of tax forms
- File your tax return on time to avoid penalties
By staying organized and informed, you can make the tax season a little less stressful.
Conclusion
 The 1099 form is an important tax form that you may encounter if you receive income other than wages, salaries, and tips. By understanding how this form works and how it differs from other tax forms, you can properly report your income and avoid any penalties. Remember to keep accurate records and file your tax return on time to make the tax season as stress-free as possible.
The 1099 form is an important tax form that you may encounter if you receive income other than wages, salaries, and tips. By understanding how this form works and how it differs from other tax forms, you can properly report your income and avoid any penalties. Remember to keep accurate records and file your tax return on time to make the tax season as stress-free as possible.